Gonorrhea: Catching and Treating “The Clap”
 By: by Amino Science
By: by Amino Science

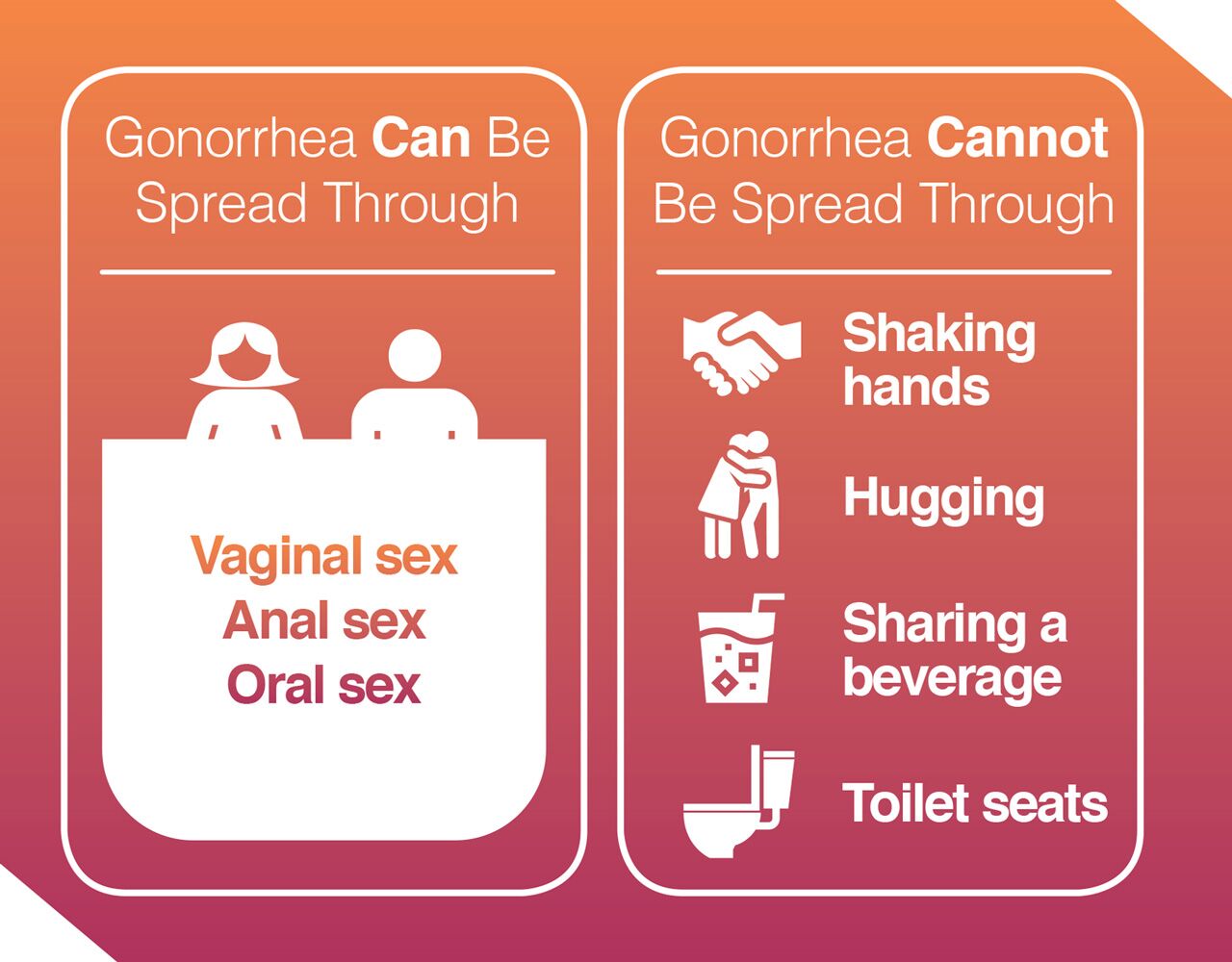
Gonorrhea, also known as “the clap,” is a sexually transmitted infection, or STI, that is spread through sexual contact including vaginal sex, anal sex, and oral sex. Gonorrhea is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which can cause a bacterial infection in multiple parts of the body including the genitals, the rectum, and the throat. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), gonorrhea is an extremely common sexually transmitted disease and most often affects young people between the ages of 15 and 24.
Gonorrhea Causes
Gonorrhea is caused when the bacteria, Neisseria gonorrhea, enters into the body through some form of sexual contact. Gonorrhea can be transmitted from one partner to another even if the penis or tongue is not inserted all the way into the other person’s body. All it takes to become infected is contact with the secretions of an infected person. Secretions can be in the form of semen, saliva, or vaginal secretions.
Once contracted, gonorrhea may be spread from one part of the body to another. For example, if a woman contracted vaginal gonorrhea, she may spread it to the anus while wiping with toilet paper. Gonorrhea must be transmitted from one person to another through intimate contact such as vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It cannot be transmitted casually through shaking hands, hugging, or from a toilet seat.
Gonorrhea Symptoms
Sometimes gonorrhea is present without any symptoms. When symptoms of gonorrhea are present, they do vary slightly for men and women. According to the CDC, signs of gonorrhea in men may include the following symptoms:
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Discharge from the penis that is white, yellow, or green
- Swollen or painful testicles
Many women who contract gonorrhea do not have symptoms or have symptoms that are mistaken for other conditions such as a bladder or vaginal infection. Common signs of gonorrhea in women may include the following symptoms:
- Painful or burning sensation while urinating
- Increase in vaginal discharge
- Smelly vaginal discharge
- Vaginal bleeding in between periods
- Pelvic pain or abdominal pain
If gonorrhea has been contracted through anal sex, it may also show no symptoms. However, when symptoms are present, they are typically the same in both men and women. Common symptoms of rectal gonorrhea include:
- Anal itching
- Soreness
- Discharge
- Bleeding
- Painful bowel movements
In addition to vaginal and anal sex, gonorrhea can be transmitted through oral sex, regardless of whether it was given or received. Symptoms of an oral gonorrhea infection in men and women may include a red, itchy, or sore throat.
If any of these symptoms are present or if a sexual partner has advised that he or she has gonorrhea, a trip to the doctor is critical to get treatment and avoid any potential complications. Untreated gonorrhea may lead to serious health issues such as infertility and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) in women when it spreads to the uterus or fallopian tubes. If PID is not treated it can impair fertility and cause ectopic pregnancy in which the fetus matures outside the uterus, normally in the fallopian tubes.
Sometimes a urine test can be used to detect the presence of gonorrhea, while other times the health care provider will take a swab sample from the infected area.

Gonorrhea Treatment
Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection that can be treated with antibiotics. Most cases of gonorrhea are responsive to antibiotics, however, according to the American Sexual Health Association, some strains of gonorrhea have been shown to be resistant to antibiotics. This resistance is the reason that most cases of gonorrhea are treated with two antibiotics. One antibiotic is given as an injection while the other antibiotic is given as an oral medication, usually in the form of a single dose pill. To ensure the gonorrhea infection gets fully treated, the American Sexual Health Association recommends the following steps to take during treatment:
- Take all medications as directed.
- Tell all sexual partners about your infection so they may be tested and treated.
- Avoid sexual contact until you and all your sex partners have been treated and cured.
- If symptoms persist after treatment is completed, get tested again.
- If you were treated with a non-recommended course of antibiotics, for instance in case of an allergy, get tested again 1 week after treatment, even if no symptoms are still present.
- Boost your immune system with essential amino acids
Gonorrhea and Pregnancy
Whether gonorrhea was contracted prior to pregnancy or during pregnancy, the infection can lead to serious complications. If gonorrhea is left untreated during pregnancy, risks include miscarriage and premature birth. Gonorrhea may also be passed from a mother to a baby during pregnancy and during vaginal birth. If it is passed to the baby, it can lead to a dangerous eye infection and pneumonia in the infant.
The good news is that there is an antibiotic for gonorrhea that is considered safe for use during pregnancy. The antibiotic can help clear the infection and protect the mother and baby. If pregnant or planning to become pregnant, it is critical to get a full STI screening to avoid unnecessary health problems and stay on top of your sexual health.

Up to 25% off Amino
Shop NowTAGS: conditions
Join the Community
Comments (0)
Most Craveable Recipes


 833-264-6620
833-264-6620



















