SI Joint Pain: How to Identify and Relieve Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 By: by Amino Science
By: by Amino Science
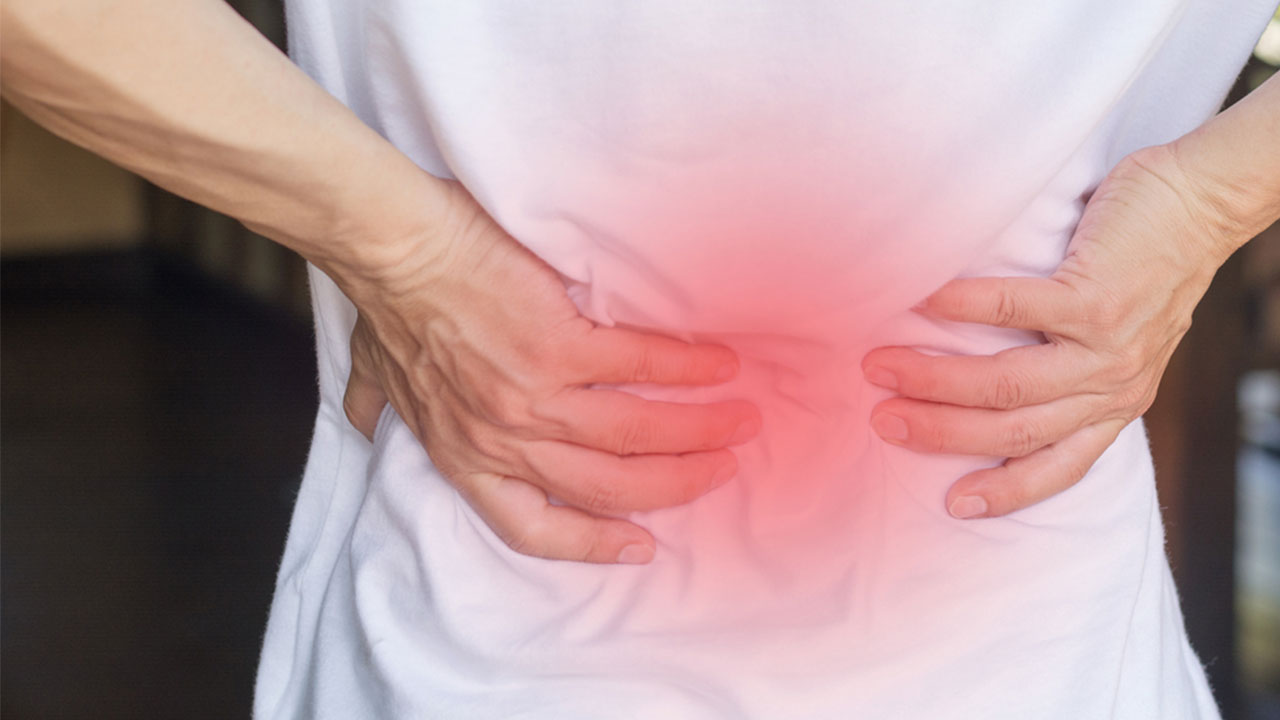
Your sacroiliac or SI joints are located in your lower back, and may be the source of low back pain you experience. This article has information that will help you identify SI joint pain. We're also covering the different methods of pain relief and treatment options.
Where Is the SI Joint?
Issues with the sacroiliac joints are thought to be the cause of 15-30% of chronic lower back pain cases. A problem at your SI joint may manifest as a radiating stabbing pain between your pelvis and hips, or it may be felt as numbness and tingling down your thighs that makes it feel as if your legs are going to buckle. That is because your SI joints are located just above your tailbone (coccyx), between the triangle-shaped bone at the base of your spine (the sacrum) and two of your three hip bones (the flared ones that jut out below your waist, known plurally as your ilia), which reside at the uppermost part of your pelvis.

The Symptoms of SI Joint Pain
SI joint pain, sometimes referred to as sacral pain, affects around 80% of adults in the United States at some point in their lives. Lower back pain and injury is one of the most common causes of work-related disabilities as well, most likely because the SI joint is the fulcrum of your back, responsible for distributing your body's weight over the pelvic region and acting as a shock absorber for your spine.
The space between the jagged SI joint bones is full of lubricating fluid and free nerve endings that send pain signals directly to the brain. When there is any misalignment in the SI joint, the pain can be debilitating, and the communication between the nerves may be interrupted, causing numbness or lack of feeling.
While the bones in this area are stabilized by strong ligaments and muscle connections that allow us to stand upright, unlike our ape ancestors, and give birth to the large craniums of human babies, the area is nevertheless extremely vulnerable to injury and other medical conditions.
Some common symptoms of SI joint pain include:
- Lower back pain
- Pain in the hips, groin, or buttocks
- Radiating pain that spreads down to the thighs
- Stiffness or burning feelings in the pelvis
- Numbness or weakness
- A sensation of leg-buckling
- Increased pain when standing from a seated position
SI Joint Pain: What Are the Causes?
There are many ways the SI joint can experience pain, only one of which is injury. Inflammation of the SI joint is called sacroiliitis, though it is often referred to as sacroiliac joint dysfunction, a general umbrella term that could apply to any of the following causes of SI joint pain.
1. Injury
The lower back is one of the most vulnerable parts of our bodies. Our brains are protected by our skulls, our most vital organs all guarded by our ribs or cradled by our pelvic bones, but the lower back region is wide-open. This allows for a unique range of motion and the ability to stand upright and tall, but it also means that the weight of the world relies on one column of bone and ligaments (the spine), which sits atop the sacroiliac joint. Trauma resulting from motor vehicle accidents, household or workplace falls, or even sudden twists of movement can cause injuries and damage that may persist for a lifetime.
2. Pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's SI joint needs to become more elastic to allow for a vaginal birth. This is achieved with the release of a hormone aptly called relaxin, which allows the pelvis to widen when it comes time to give birth.
A combination between this elasticity, plus the weight gain associated with pregnancy and the positioning of the baby's body, all lead to a higher likelihood of SI injury or ache. The joint becomes less stable, and some women even develop arthritis in their SI joints, a condition that may worsen with subsequent pregnancies.
3. Gait
Your walking pattern or gait can contribute to SI joint pain and dysfunction. For example, an overpronation problem can affect the way you walk, and the same is true if one leg happens to be longer than the other. A lifetime of irregular walking can add up to problems like shin splints, knee joint pain, and lower back pain, conditions that may or may not be remedied by corrective footwear.
4. Gout
Gouty arthritis, or simply gout, is a disease characterized by high levels of uric acid in the body, often caused by poor diet and lifestyle choices. The joint pain caused by uric acid buildup can be severe, and while it usually starts with the joint of the big toe, it can affect any joint, including the two SI joints.
5. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis involves the degeneration of joint cartilage, causing potential pain and stiffness in many joints, including the SI joint, the knees, hips, and thumbs.
6. Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis that affects the joints of the spine. Not only does it cause pain from inflammation, but it can also lead to the growth of new bone structures that fuse together spinal joints and inhibit normal movement. This condition primarily affects the SI joint, but it can also cause inflammation in other joints and organs as far away as the eyes. It is most likely to be diagnosed in young men.
Diagnosing SI Joint Issues
SI joint problems are often hard to diagnose. These joints are located deep in your body and their associated issues often cannot be seen on CT, MRI, or X-ray images. Another reason is that lower back pain and other signs of SI issues resemble the symptoms of different conditions like arthritis of the hip, bulging spinal disks, and sciatica.
Doctors may diagnose your SI joint problems with a:
- Physical exam: The doctor may move you or ask you to stretch in certain ways to identify the source of your pain.
- Diagnostic injection: By injecting a local anesthetic like lidocaine into the SI region, doctors may determine the source of your pain if it temporarily disappears upon injection at that site.
- Imaging test: While X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs don't show every potential cause of SI joint pain, they can reveal an injury or misalignment right away.
SI Joint Pain: Treatment Options
Here are some possible options for treating pain in your SI joints.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
- Pain medication: Doctors may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids to help relieve joint inflammation and chronic SI pain that cannot otherwise be prevented.
- Chiropractic or physical therapy: A physical therapist or chiropractic physician may perform or instruct you in SI joint stretches to relieve pain and build strength.
- Yoga: The stretching exercises that characterize yoga can help increase flexibility and improve your pain symptoms.
- SI joint injections: Medications like corticosteroids may be regularly injected into the affected SI joint or joints to ease pain.
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA): This procedure, like steroid injections, can help temporarily deaden certain sensory nerves to stop the transmission of pain signals from the SI joints.
- Physical aids: A sacroiliac belt or corrective footwear could help SI joint pain depending on its cause.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery is the very last resort when it comes to relieving sacroiliac pain, and involves a sacroiliac joint fusion surgery that utilizes small screws and plates to encourage these bones to fuse together. It's invasive, it comes with its own set of risks (as does any major surgery), and experts agree it's best to explore all other nonsurgical options before deciding alongside your doctor that this is the only way forward.
Preventing and Recovering from SI Joint Pain
Some instances of SI joint pain are temporary, say if it's caused by a pregnancy or can be dealt with by wearing corrective gear. However, sometimes this pain arises from chronic medical conditions like osteoarthritis or irreversible injury, and may plague you for a much longer time without medical intervention. Nutritional aids such as supplemental essential amino acids have been proven to accelerate recovery and outcomes.
Be cautious with your back when lifting or moving items at home or at work, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to avoid conditions like gout. That being said, not all SI joint pain causes can be avoided, so consult with a trusted medical professional to recover the best way possible.


Up to 25% off Amino
Shop NowTAGS: conditions
Join the Community
Comments (0)
Most Craveable Recipes


 833-264-6620
833-264-6620



















